Hero stories
Rapid success
stories
Inspiring stories of healthcare professionals providing care and changing patient lives

Serving a veteran on Veterans Day
See how doctors at Stony Brook Medicine saved a Veteran’s life by using Rapid CTP to uncover what others may have overlooked.

Climbing to the top
Learn how one healthcare team—equipped with RapidAI technology—was able to save a mountaineer's life in record-breaking time following a severe stroke.

A race against time
How a mother’s care team defied odds to deliver timely treatment despite ambulance strikes.
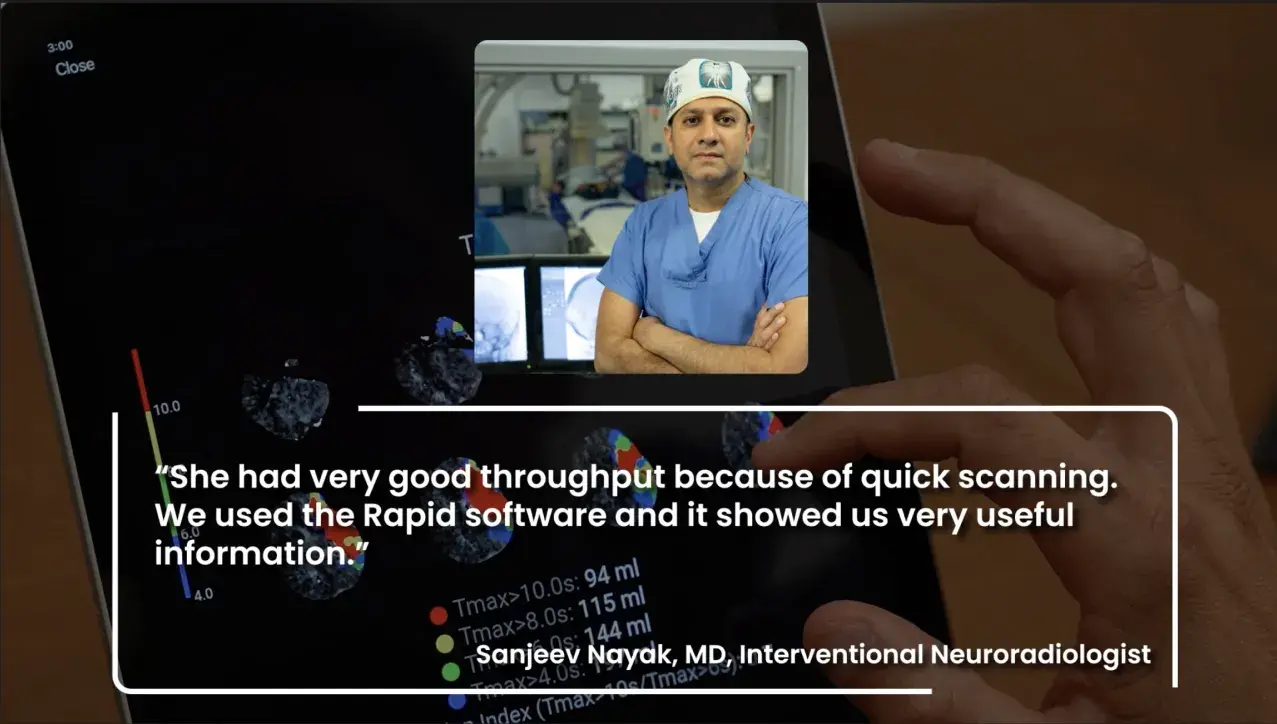
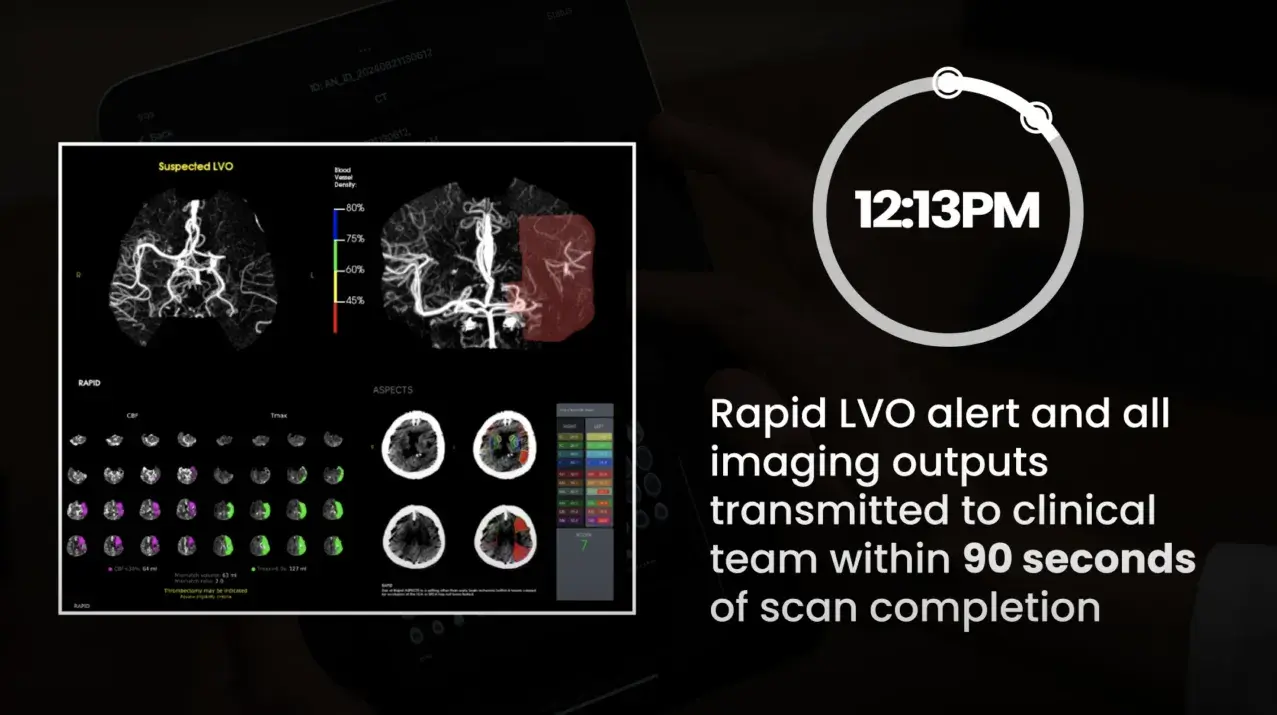
Team activation in minutes with RapidAI: PSC to CSC
RapidAI helps the stroke care team achieve one of the best times for door at a PSC to recanalization at a CSC—with patient recovery starting at just 91 minutes after arrival.
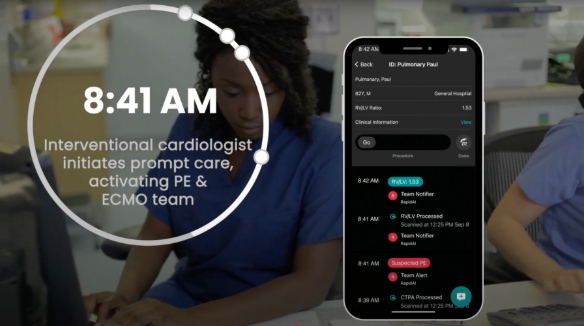
From hours to minutes: Prompt PE activation
See how critical time is saved leading to improved patient outcomes.